Transarterial treatments are highly effective and minimally invasive procedures that are used to treat primary liver tumors. These tumors originate within the liver and accessing the blood vessels that supply the tumor with blood is an essential part of the procedure. Therapy is then delivered directly to the tumor site, ensuring optimal results and minimal discomfort for the patient.
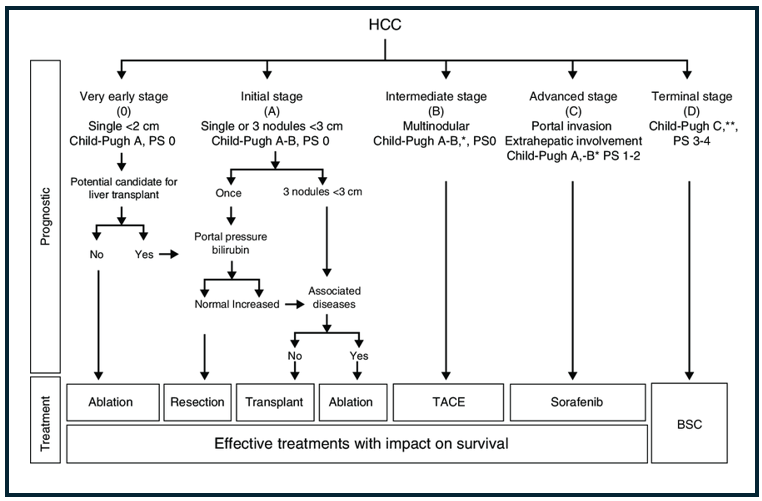
BCLC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Group) Classification
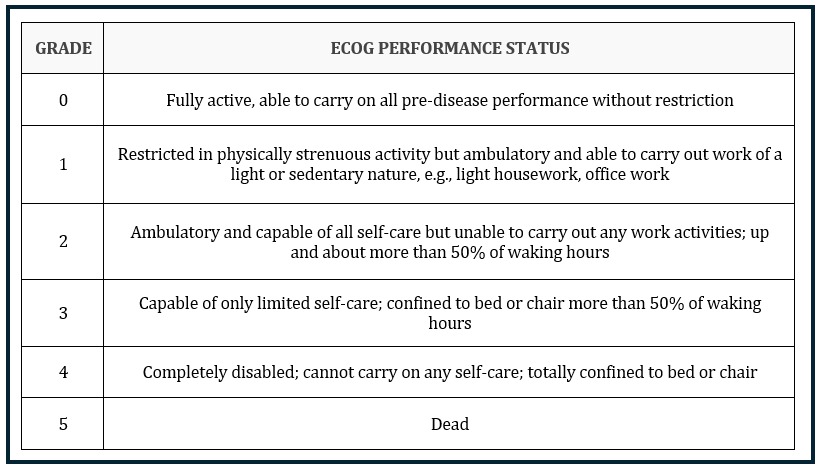
ECOG Performance Classification
Available Techniques
- Conventional transarterial chemoebolization (TACE)
- Drug-eluting Beads transarterial chemoembolization (DEB-TACE)
- Catheter-directed superselective intrahepatic treatment using coaxial microcatheters
- Access via inguinal artery in local anesthesia and general analgesia with sedation.
Liver tumors
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatoma, HCC)
- Intrahepatic peripheral cholangiocarcinoma (CCC)
Treatment Indications for Patients with HCC
- No surgical option
- Bridging to liver transplantation
- BCLC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Group) stage B (intermediate) and C (advanced)*
BCLC-Stage B: single or multinodular HCC, performance status 0
BCLC-Stage C: single or multinodular HCC, small portal vein, but no major portal vein infiltration, no proven metastases, ECOG-performance status 1-2* - Main portal vein open
- Child-Pugh Class A and B (no Child-Pugh Class C)
Treatment Indications for Patients with CCC
- No surgical option
- Systemic chemotherapy ineffective or not tolerated
- Main portal vein open
- No proven extrahepatic metastases
- If cirrhosis present, Child-Pugh Class A and B (no Child-Pugh Class C)
Supportive and Medical Treatment
- Accompanying oncological therapy
- Pain management
- Supportive treatment
Further Options
- Update in imaging by CT and MRT concerning staging of tumor disease
- Evaluation of surgical options on demand and in cooperation with University hospital